位置:首页 > 安全分类 > WEB安全
AFL之自定义mutator开发分析
前言:
什么是mutator?
通过使用根据给定语法执行突变的库来启用结构感知模糊测试,进而达成更细致化模糊数据处理的第三方组件,一般由模糊测试人员自己开发编写。
在什么环境下需要mutator?
对于xml等固定文件格式的testcase时就需要编写mutator进行精细化fuzzing。
为什么要用python编写mutator?
xml型mutator因为python库更加齐全,所以我们使用python来编写mutator
我们先来看看afl对mutator的调用流程:
下面是C library版mutator函数afl_custom_fuzz和afl_custom_init和python版fuzz和init本质上是一样的
afl_custom_fuzz调用分析:
60分钟仍然一个cycle都没有找到时,会在env上设置AFL_EXPAND_HAVOC_NOW

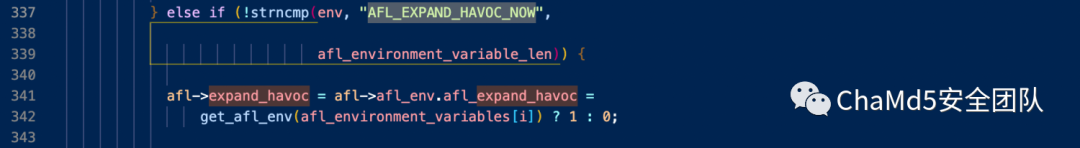
然后在分析到env存在AFL_EXPAND_HAVOC_NOW后,将afl->expand_havoc设置为1

当afl->expand_havoc为1时,afl->limit_time_sig = -1
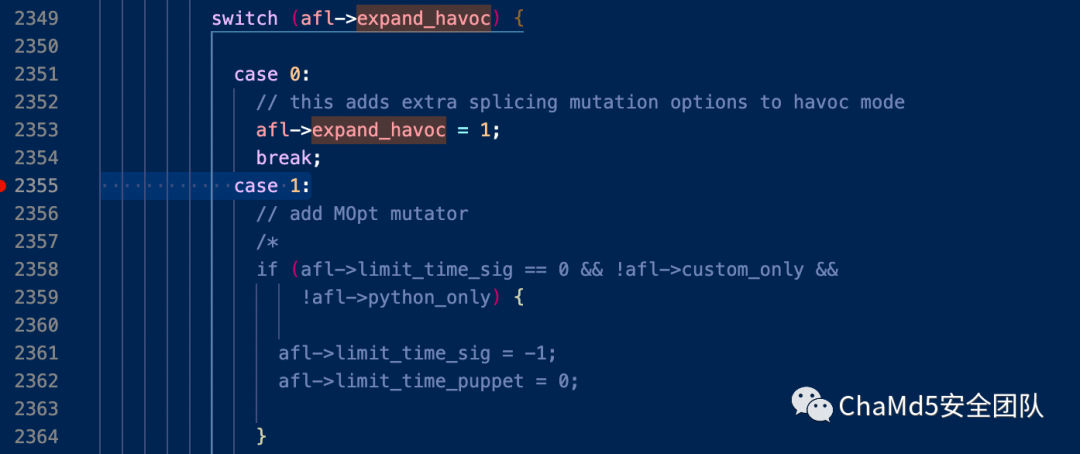
确定afl->limit_time_sig <= 0就执行fuzz_one_original()

然后调用到afl_custom_fuzz

6.png
上面的el->data即为我们-i 指定目录内部文件的testcase,然后经过自定义mutator来生成自己的testcase
afl_custom_init调用分析:
调用流程:
setup_custom_mutatorsload_custom_mutatorafl_custom_init



然后给我们的mutator配置包装好了的afl_t结构体*afl和随机数种子seed
开发流程:
根据官方开发文档:Custom Mutators | AFLplusplus 可以知道我们需要定义一个init()来初始化配置我们的seed来保证我们的mutator上的rand随机性和afl上的rand是同步的。总的来说是调用了lxml来编写xml型的mutator:
from lxml import etree as ET
配置初始化函数init():
def init(seed):
"""
Called once when AFL starts up. Seed is used to identify the AFL instance in log files
"""
global __mutator__ #定义一个类
global __seed__ #定义一个全局随机种子
# Get the seed
__seed__ = seed #根据afl传入的seed重写我们的seed
# Create a global mutation class
try:
__mutator__ = XmlMutatorMin(__seed__, verbose=__log__) #初始化类
log("init(): Mutator created")
except RuntimeError as e:
log("init(): Can't create mutator: %s" % e.message)
注意这里的__mutator__ = XmlMutatorMin(__seed__, verbose=__log__)就是我们fuzz调用到的函数。然后进入到XmlMutatorMin.py上调用__init__来初始化XmlMutatorMin类:
class XmlMutatorMin:
"""
Optionals parameters:
seed Seed used by the PRNG (default: "RANDOM")
verbose Verbosity (default: False)
"""
def __init__(self, seed="RANDOM", verbose=False):
""" Initialize seed, database and mutators """
# Verbosity
self.verbose = verbose
# Initialize PRNG
self.seed = str(seed)
if self.seed == "RANDOM":
random.seed()
else:
if self.verbose:
print("Static seed '%s'" % self.seed)
random.seed(self.seed)
# Initialize input and output documents
self.input_tree = None
self.tree = None
# High-level mutators (no database needed)
hl_mutators_delete = [
"del_node_and_children",
"del_node_but_children",
"del_attribute",
"del_content",
] # Delete items
hl_mutators_fuzz = ["fuzz_attribute"] # Randomly change attribute values
# Exposed mutators
self.hl_mutators_all = hl_mutators_fuzz + hl_mutators_delete
上面的self.hl_mutators_all就是我们mutator对从afl传入数据进行模糊处理的函数列表。然后还需要一个deinit()来结束初始化:
def deinit(): # optional for Python pass
配置数据模糊函数fuzz():
buf:传入的数据
def fuzz(buf, add_buf, max_size):
"""
Called for each fuzzing iteration.
"""
global __mutator__
# Do we have a working mutator object?
if __mutator__ is None:
log("fuzz(): Can't fuzz, no mutator available")
return buf
# Try to use the AFL buffer
via_buffer = True
# Interpret the AFL buffer (an array of bytes) as a string
if via_buffer:
try:
buf_str = str(buf)
log("fuzz(): AFL buffer converted to a string")
except Exception:
via_buffer = False
log("fuzz(): Can't convert AFL buffer to a string")
# Load XML from the AFL string
if via_buffer:
try:
__mutator__.init_from_string(buf_str)
log(
"fuzz(): Mutator successfully initialized with AFL buffer (%d bytes)"
% len(buf_str)
)
except Exception:
via_buffer = False
log("fuzz(): Can't initialize mutator with AFL buffer")
# If init from AFL buffer wasn't succesful
if not via_buffer:
log("fuzz(): Returning unmodified AFL buffer")
return buf
# Sucessful initialization -> mutate
try:
__mutator__.mutate(max=5)
log("fuzz(): Input mutated")
except Exception:
log("fuzz(): Can't mutate input => returning buf")
return buf
# Convert mutated data to a array of bytes
try:
data = bytearray(__mutator__.save_to_string())
log("fuzz(): Mutated data converted as bytes")
except Exception:
log("fuzz(): Can't convert mutated data to bytes => returning buf")
return buf
# Everything went fine, returning mutated content
log("fuzz(): Returning %d bytes" % len(data))
return data
上述代码对从afl传入的buf进行了4步处理:
一、格式化输出afl传入的buf:
buf_str = str(buf)
二、将xml流构造成树:
__mutator__.init_from_string(buf_str)
三、对已经被构造成树的数据流数据进行模糊操作:
max表示了对数据处理的最大次数
__mutator__.mutate(max=5)
四、将模糊处理后的xml树数据保存成testcase:
data = bytearray(__mutator__.save_to_string())
init_from_string:
对传入的xml流重构成tree,进而更好的对数据进行处理
def init_from_string(self, input_string):
""" Initialize the mutator from a XML string """
# Get a pointer to the top-element
self.input_tree = self.__parse_xml(input_string)
# Get a working copy
self.tree = deepcopy(self.input_tree) # 使用deepcopy生成一个用于处理数据的临时树
def __parse_xml(self, xml):
""" Parse an XML string. Basic wrapper around lxml.parse() """
try:
tree = ET.parse(io.BytesIO(xml)) # 使用了lxml.etree.parse对传入的xml流重构成树
except ET.ParseError:
raise RuntimeError("XML isn't well-formed!")
except LookupError as e:
raise RuntimeError(e)
# Return a document wrapper
return tree
mutate:
对xml数据进行模糊处理类型可以分为:
- 删除结点但是保存子结点
- 删除结点但是不保存子结点
- 删除属性
- 删除内容
- 对属性数据进行模糊处理
一、保证模糊处理函数调用的随机性:
def mutate(self, min=1, max=5): """ Execute some high-level mutators between $min and $max times, then some medium-level ones """ # High-level mutation self.__exec_among(self, self.hl_mutators_all, min, max) def __exec_among(self, module, functions, min_times, max_times): """ Randomly execute $functions between $min and $max times """ for i in xrange(random.randint(min_times, max_times)): # Function names are mangled because they are "private" getattr(module, "_XmlMutatorMin__" + random.choice(functions))()
min和max保证了调用数据模糊处理的次数随机性(即调用多少次对数据的处理操作) __exec_among保证了对数据模糊处理的类型随机性(即随机选择上面的模糊处理类型操作)
二、删除结点:
def __del_node(self, delete_children):
""" Called by the __del_node_* mutators """
# Select a node to modify (but the root one)
(rand_elem_id, rand_elem) = self.__pick_element(exclude_root_node=True)
# If the document includes only a top-level element
# Then we can't pick a element (given that "exclude_root_node = True")
# Is the document deep enough?
if rand_elem is None:
if self.verbose:
print("Can't delete a node: document not deep enough!")
return
# Log something
if self.verbose:
but_or_and = "and" if delete_children else "but"
print(
"Deleting tag #%i '%s' %s its children"
% (rand_elem_id, rand_elem.tag, but_or_and)
)
if delete_children is False:
# Link children of the random (soon to be deleted) node to its parent
for child in rand_elem:
rand_elem.getparent().append(child)
# Remove the node
rand_elem.getparent().remove(rand_elem)
调用了lxml.etree.getparent()获取到当前结点的父结点,进而删除node 如果delete_children为true则调用lxml.etree.append()将子node附加到父node的上一个node 如果delete_children为false则调用lxml.etree.remove()将整个父node删除
保存子结点:
def __del_node_and_children(self): """High-level minimizing mutator Delete a random node and its children (i.e. delete a random tree)""" self.__del_node(True)
不保存子结点:
def __del_node_but_children(self): """High-level minimizing mutator Delete a random node but its children (i.e. link them to the parent of the deleted node)""" self.__del_node(False)
三、删除属性:
def __del_attribute(self):
"""High-level minimizing mutator
Delete a random attribute from a random node"""
# Select a node to modify
(rand_elem_id, rand_elem) = self.__pick_element()
# Get all the attributes
attribs = rand_elem.keys()
# Is there attributes?
if len(attribs) < 1:
if self.verbose:
print("No attribute: can't delete!")
return
# Pick a random attribute
rand_attrib_id = random.randint(0, len(attribs) - 1)
rand_attrib = attribs[rand_attrib_id]
# Log something
if self.verbose:
print(
"Deleting attribute #%i '%s' of tag #%i '%s'"
% (rand_attrib_id, rand_attrib, rand_elem_id, rand_elem.tag)
)
# Delete the attribute
rand_elem.attrib.pop(rand_attrib)
使用lxml.etree.attrib.pop()删除node里面的某一属性四、删除内容:
def __del_content(self):
"""High-level minimizing mutator
Delete the attributes and children of a random node"""
# Select a node to modify
(rand_elem_id, rand_elem) = self.__pick_element()
# Log something
if self.verbose:
print("Reseting tag #%i '%s'" % (rand_elem_id, rand_elem.tag))
# Reset the node
rand_elem.clear()
使用lxml.etree.clear()删除node内的content五、对属性数据进行模糊处理:
def __fuzz_attribute(self):
""" Fuzz (part of) an attribute value """
# Select a node to modify
(rand_elem_id, rand_elem) = self.__pick_element()
# Get all the attributes
attribs = rand_elem.keys()
# Is there attributes?
if len(attribs) < 1:
if self.verbose:
print("No attribute: can't replace!")
return
# Pick a random attribute
rand_attrib_id = random.randint(0, len(attribs) - 1) # 随机获取属性id
rand_attrib = attribs[rand_attrib_id] # 获取知道属性id指向的属性
# We have the attribute to modify
# Get its value
attrib_value = rand_elem.get(rand_attrib) # 获取指定属性的数据
# print("- Value: " + attrib_value)
# Should we work on the whole value?
func_call = "(?P[a-zA-Z:\-]+)\((?P.*?)\)"
p = re.compile(func_call)
l = p.findall(attrib_value)
if random.choice((True, False)) and l:
# Randomly pick one the function calls
(func, args) = random.choice(l)
# Split by "," and randomly pick one of the arguments
value = random.choice(args.split(","))
# Remove superfluous characters
unclean_value = value
value = value.strip(" ").strip("'")
# print("Selected argument: [%s]" % value)
else:
value = attrib_value
# For each type, define some possible replacement values
choices_number = (
"0",
"11111",
"-128",
"2",
"-1",
"1/3",
"42/0",
"1094861636 idiv 1.0",
"-1123329771506872 idiv 3.8",
"17=$numericRTF",
str(3 + random.randrange(0, 100)),
)
choices_letter = (
"P" * (25 * random.randrange(1, 100)),
"%s%s%s%s%s%s",
"foobar",
)
choices_alnum = (
"Abc123",
"020F0302020204030204",
"020F0302020204030204" * (random.randrange(5, 20)),
)
# Fuzz the value
if random.choice((True, False)) and value == "":
# 为NULL不管
new_value = value
elif random.choice((True, False)) and value.isdigit():
# number用number替代
new_value = random.choice(choices_number)
elif random.choice((True, False)) and value.isalpha():
# 文本用文本替代
new_value = random.choice(choices_letter)
elif random.choice((True, False)) and value.isalnum():
# 字母数字就用字母数字替代
new_value = random.choice(choices_alnum)
else:
# Default type
new_value = random.choice(choices_alnum + choices_letter + choices_number)
# If we worked on a substring, apply changes to the whole string
if value != attrib_value:
# No ' around empty values
if new_value != "" and value != "":
new_value = "'" + new_value + "'"
# Apply changes
new_value = attrib_value.replace(unclean_value, new_value)
# Log something
if self.verbose:
print(
"Fuzzing attribute #%i '%s' of tag #%i '%s'"
% (rand_attrib_id, rand_attrib, rand_elem_id, rand_elem.tag)
)
# Modify the attribute
rand_elem.set(rand_attrib, new_value.decode("utf-8"))
实质就是随机正则某个属性数据,然后使用自制字典同类型替换
真正使用的mutator要自开发python3兼容的版本,然后还要bytearrary()包含格式化输出才能正常使用。
AFL++ 调用Python Library:
export PYTHONPATH=/home/mutator/ export AFL_PYTHON_MODULE=mutator afl-fuzz ....
PYTHONPATH:指向mutator.py的路径
export AFL_PYTHON_MODULE:指定文件夹内mutator.py,注意不能有.py后缀
afl-fuzz ....:为afl-fuzz的执行命令
下一篇:安全工具集成平台-蜻蜓

 一、序言API为当今大多数数字体验提供了动力,API安全性仍然是大多数CXO最关心的问题。尽管数字化转型不断推...
一、序言API为当今大多数数字体验提供了动力,API安全性仍然是大多数CXO最关心的问题。尽管数字化转型不断推... 随着互联网的普及,网络安全变得越来越重要。Java等程序员需要掌握基本的web安全知识,防患于未然,下面列举一些...
随着互联网的普及,网络安全变得越来越重要。Java等程序员需要掌握基本的web安全知识,防患于未然,下面列举一些... 29岁转行网络安全,这个选择合适吗?在当今数字化时代,网络安全已成为一个越来越受到人们关注的领域。越来越多的...
29岁转行网络安全,这个选择合适吗?在当今数字化时代,网络安全已成为一个越来越受到人们关注的领域。越来越多的... 想象一下,你正准备在网上进行一次重要的银行转账,你打开了看似官方的网站,输入了你的账号和密码。然而,你并不知...
想象一下,你正准备在网上进行一次重要的银行转账,你打开了看似官方的网站,输入了你的账号和密码。然而,你并不知... 2022年以来,我国网络安全行业的市场规模持续增长,根据市场调研在线网发布的2023-2029年中国网络安全集成行业...
2022年以来,我国网络安全行业的市场规模持续增长,根据市场调研在线网发布的2023-2029年中国网络安全集成行业... 2021年7月12日工信部发布的《网络安全产业高质量发展三年行动计划(2021-2023年)》,文件中提出,2023年网络安全...
2021年7月12日工信部发布的《网络安全产业高质量发展三年行动计划(2021-2023年)》,文件中提出,2023年网络安全... 在云计算、大数据、工业互联网、物联网等行业快速发展所带来的下游客户的安全需求增长下,网络安全行业迎来了...
在云计算、大数据、工业互联网、物联网等行业快速发展所带来的下游客户的安全需求增长下,网络安全行业迎来了... 网络安全行业是当下非常热门的行业之一,其不仅具有较高的关注度,也是IT行业内热议的话题,尤其是在当下,不少人都...
网络安全行业是当下非常热门的行业之一,其不仅具有较高的关注度,也是IT行业内热议的话题,尤其是在当下,不少人都...